Hip fractures are one of the most common and serious injuries in elderly men and women. They usually happen because bones become weak and fragile due to osteoporosis – a condition where bones lose strength and density. Even a small fall in the bathroom, slipping on the floor, or missing a step can cause a fracture in the hip.
These injuries not only cause pain but also affect mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. That’s why timely diagnosis and proper treatment are very important.
Why are Old People at Higher Risk?
Osteoporosis: Weak bones break easily.
Falls: Balance issues, poor vision, or weak muscles increase the risk of falling.
Medical conditions: Diabetes, arthritis, or heart problems can also play a role.
Age-related changes: Bones naturally lose strength as we grow older.
Both men and women can have hip fractures, but the risk is slightly higher in post-menopausal women due to hormonal changes that affect bone density.
Common Types of Hip Fractures
- Neck of femur fracture – Just below the ball of the hip joint.
- Intertrochanteric fracture – Slightly lower down the thigh bone.
- Subtrochanteric fracture – Below the hip joint, at the upper thigh bone.
The type of fracture and the patient’s age, bone quality, and overall health help doctors decide the best treatment.
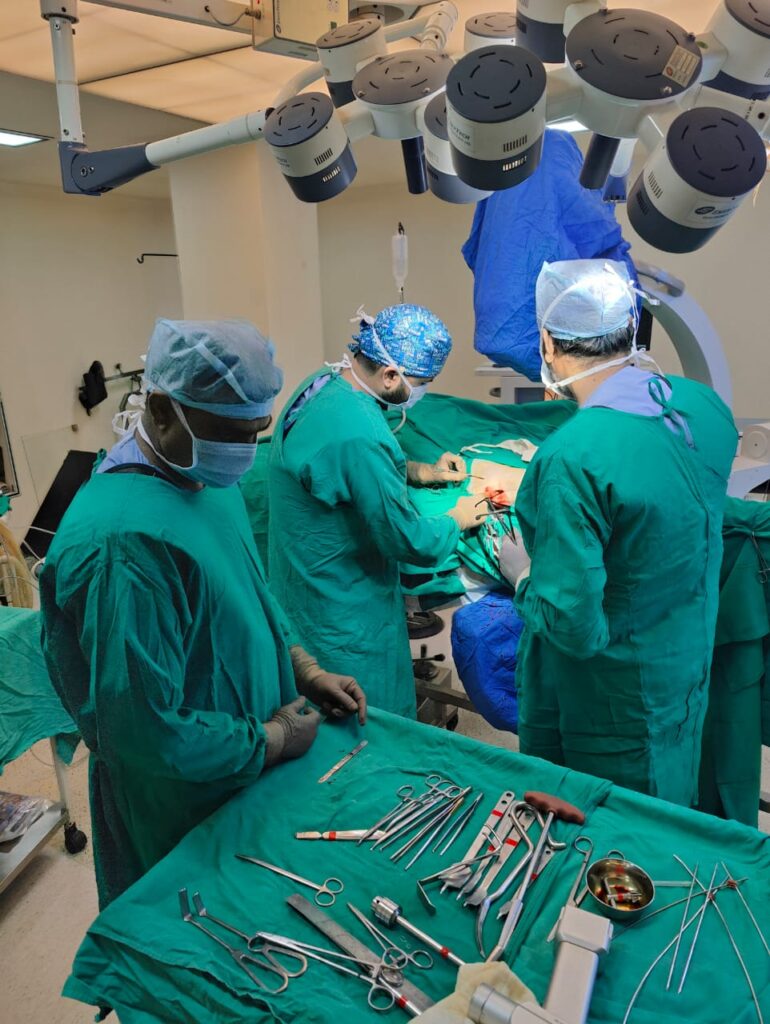
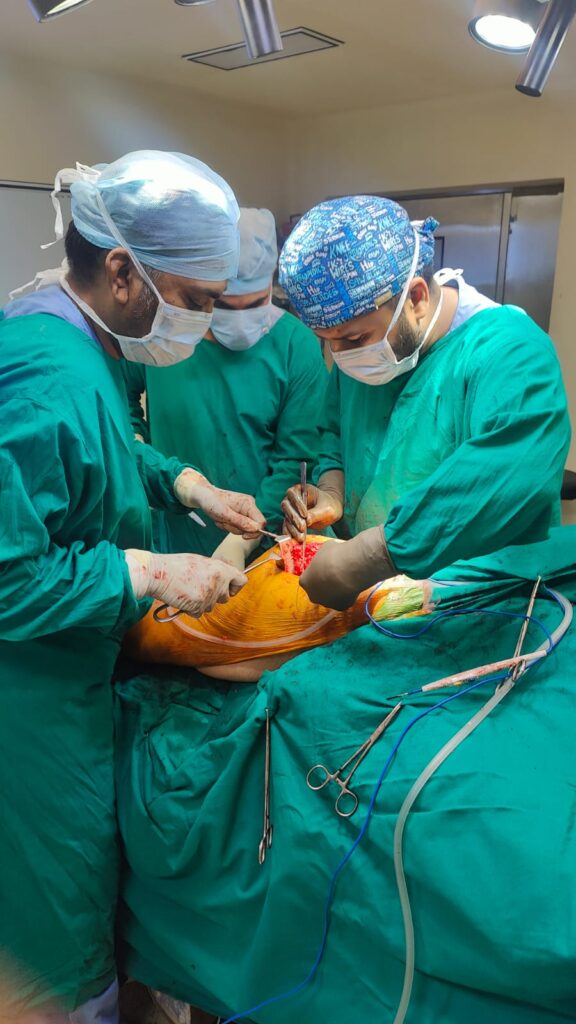
Management –
Orthopaedic surgery offers several effective ways to fix hip fractures. The main aim is to make the patient pain-free, allow early walking, and restore independence.
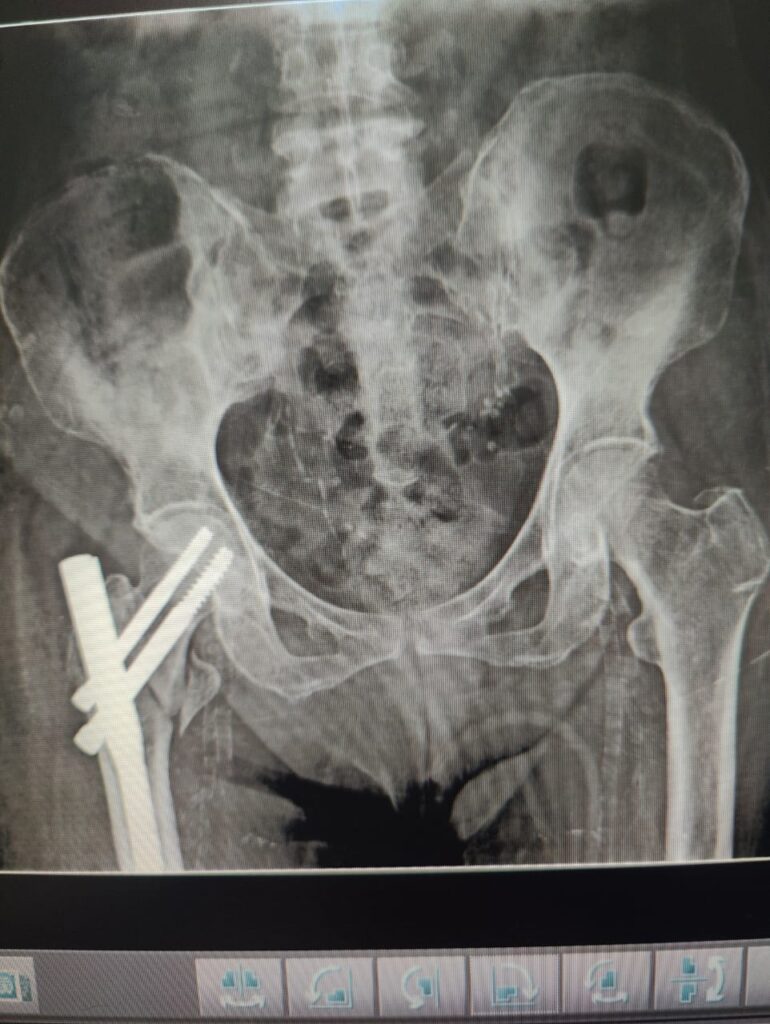
- PFN (Proximal Femoral Nail)
A metal rod is inserted into the thigh bone to stabilize the fracture.
Best suited for intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures.
Strong and allows early movement. - DHS (Dynamic Hip Screw)
A screw and plate system used to hold the broken bone in place.
Commonly used for stable intertrochanteric fractures.
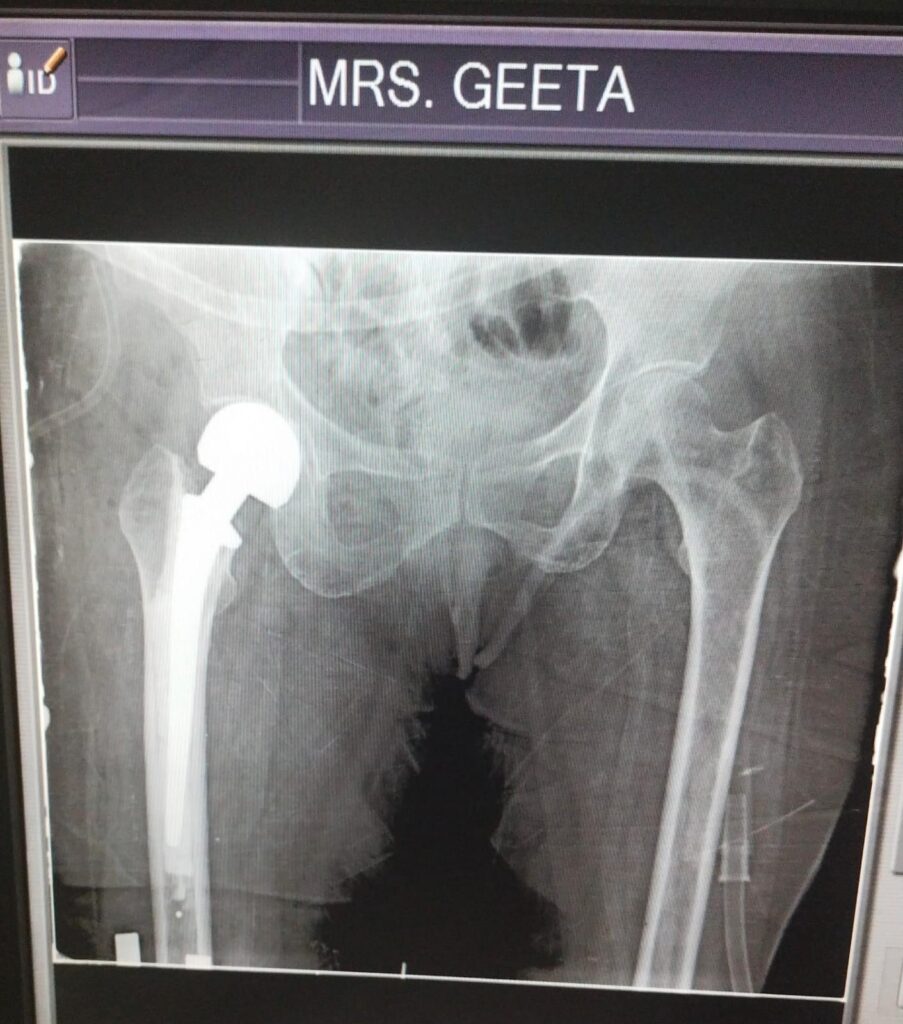
Helps the bone heal naturally over time. - Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty (Partial Hip Replacement)
The broken ball part of the hip joint is replaced with a metal implant.
Useful in elderly patients with neck of femur fractures where bone healing is difficult.
Allows patients to sit, stand, and walk quickly after surgery. - Total Hip Replacement (THR)
Both the ball and socket of the hip joint are replaced with artificial parts.
Recommended for patients with hip arthritis, severe fracture, or poor bone quality.
Provides excellent pain relief and long-term mobility.
Rehabilitation & Physio-
Surgery is just the first step. Recovery requires:
Early mobilization: Walking with support as soon as possible.
Physiotherapy: To strengthen muscles and regain movement.
Diet: Rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
Fall prevention: Using walking aids, non-slip footwear, and making homes safer.
Key Takeaway
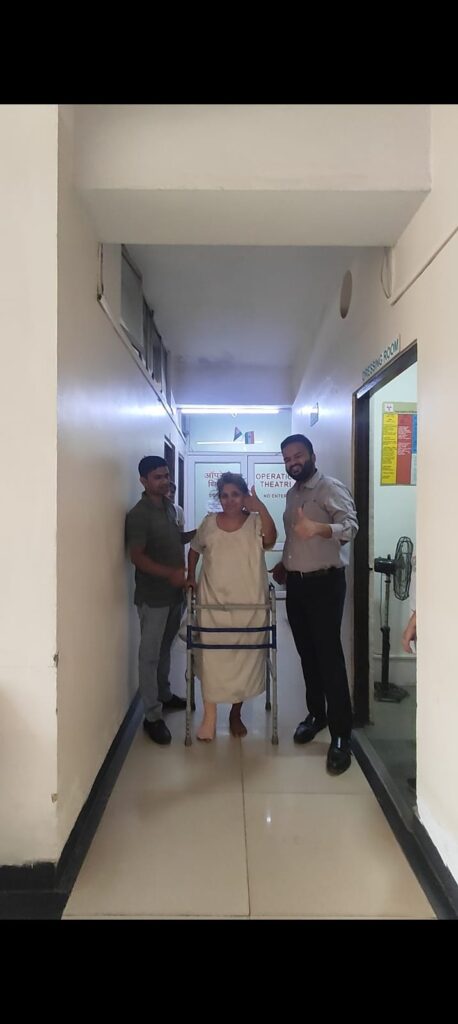
Hip fractures in elderly and osteoporotic patients need urgent medical attention. With modern surgical techniques like PFN, DHS, Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty, and Total Hip Replacement, patients can return to an active and independent life.
If you or your loved one is facing hip pain, difficulty in walking after a fall, or any signs of fracture, consult an orthopaedic specialist immediately. Early treatment gives the best outcomes.
Final Result